zkConvex - A Large-Scale Anonymous Electronic Voting Scheme Based on zk-SNARKs
A large-scale anonymous electronic voting scheme based on zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge) offers unique value and significance in ensuring the anonymity, security, and reliability of voting. zk-SNARKs is a cryptographic technology that enables one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that a statement is true, without revealing any information other than the truth of the statement itself. Applying zk-SNARKs to electronic voting brings several key advantages:
-
Protection of Voter Identity Privacy: The connection between a voter’s choice and their personal identity is not disclosed; it’s impossible to identify from public information whether a specific voter has participated. This also enhances the fairness of the voting system.
-
Prevention of Vote Buying and Selling: Voters participate under pseudonyms and are unable to prove their own voting results. This means voters cannot sell their votes to third parties who may wish to purchase them.
-
Verifiable Voting Results: Everyone can verify the voting results based on the public counting proofs.
Convex Analysis
The governance of Convex relies on the vote-locking mechanism of CVX tokens, the native token of Convex. By locking CVX, one can vote on any proposal presented on Convex (published on snapshot). This proposal regarding Curve aims to add a gauge to the crvUSD/USD+ StableSwap-ng liquidity pool on the Arbitrum chain to determine the amount of CRV tokens the pool should receive as liquidity rewards.
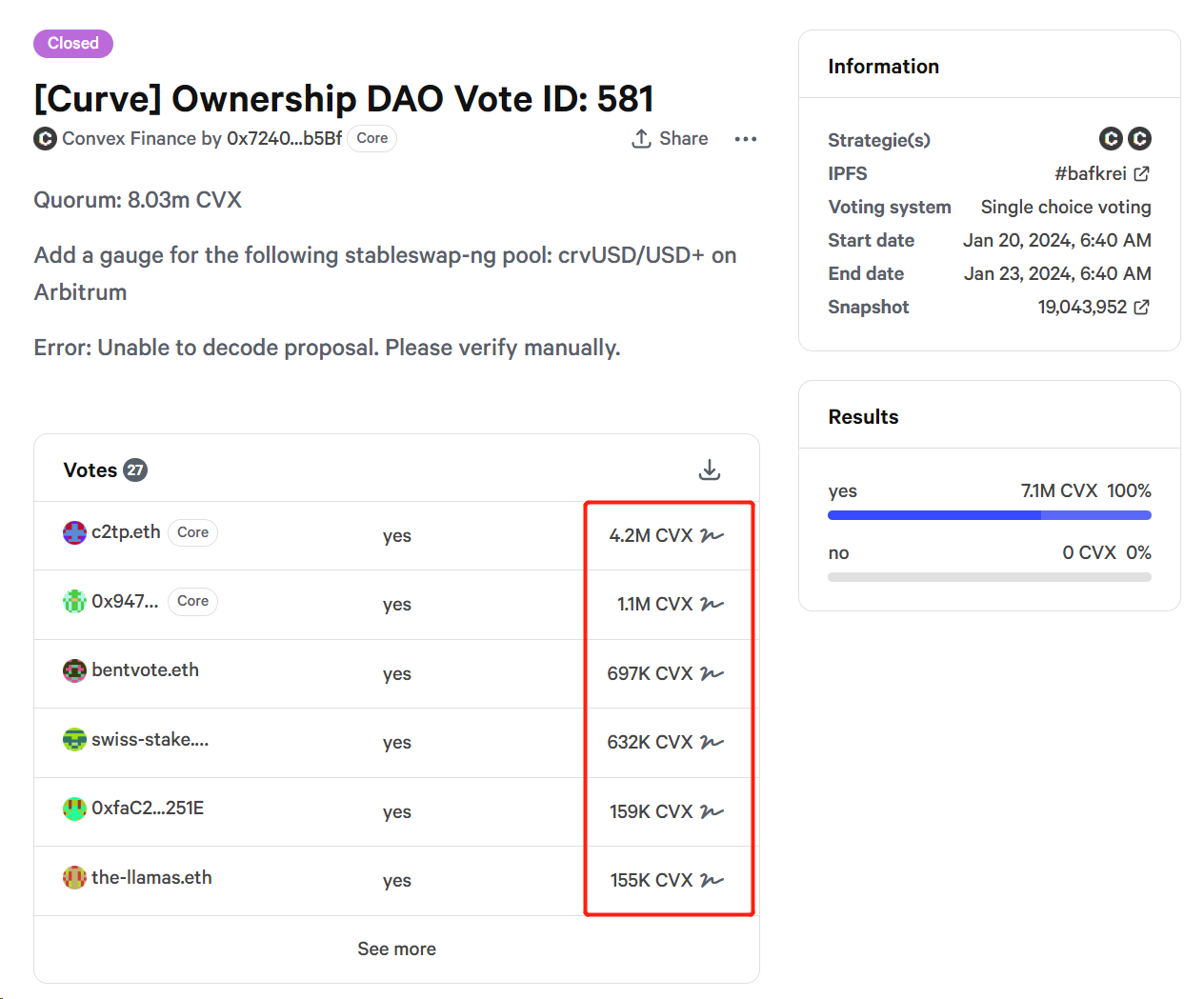
In this case, to secure more liquidity rewards for their pool, project operators need to garner more votes for this proposal. There are two ways to achieve this:
-
The project operators buy CVX and lock these CVX for voting;
-
The project operators seek other CVX holders to vote for their pool.
The first method involves the project operators buying CVX, while the second method involves buying the voting rights represented by CVX, meaning the project operators need to bribe CVX holders to vote for them. In reality, the first method is more costly than the second, so project operators tend to prefer purchasing voting rights of CVX.
However, the second method may allow project operators with more resources to gain an unfair advantage, making it difficult for smaller or newer projects to compete. To address this issue, we employ a large-scale anonymous electronic voting scheme based on zk-SNARKs to assist Convex in private governance. This scheme involves five different participants and is defined by eight related functions. The entire voting process can be divided into five stages.
Participants Composition
The electronic voting scheme involves the following five participants: Proposers, CVX Holders , Cryptographic Coordinator, Pseudonym Registrar, and Counters . Among them, proposers and CVX holders are inherent to Convex. Proposal-related information and voting results are still published on snapshot.
-
Proposers: Also known as project operators, they can initiate proposals for their liquidity pools and are also CVX holders themselves.
-
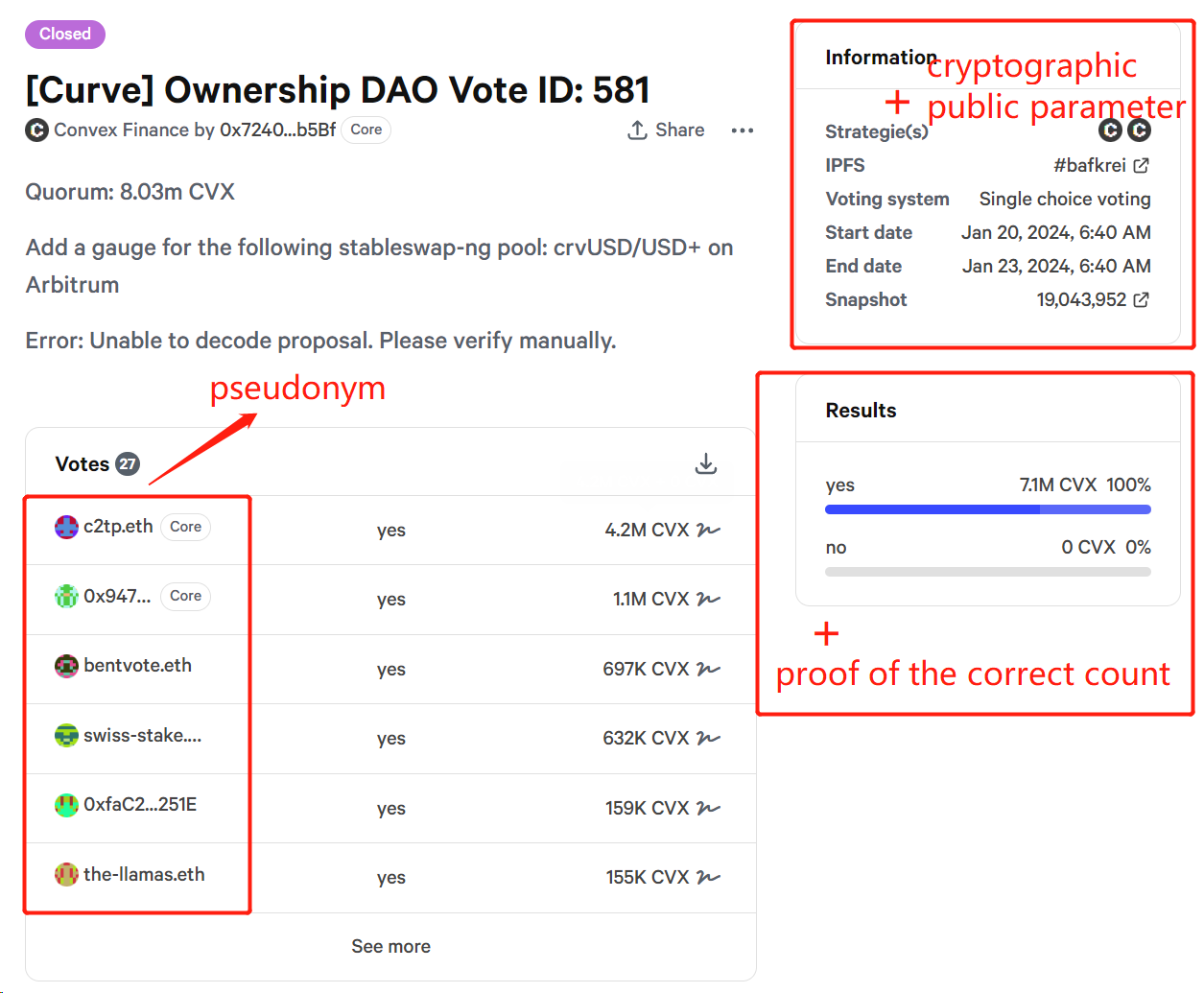
CVX Holders: Also known as voters, they can lock CVX tokens to vote. They vote under pseudonyms to ensure anonymity. As shown in the figure below, the voting results published on snapshot will not display the on-chain addresses of CVX holders, but their pseudonyms instead.
-
Snapshot: Publishes proposal information, voting information, cryptographic public parameters, voting results, and proofs of correct counting. The voting results include not only those cast by CVX holders but also null ballots cast by snapshot.
-
Cryptographic Coordinator: Responsible for generating cryptographic parameters and key pairs, and publishing the public parameters on snapshot.
-
Pseudonym Registrar: Registers pseudonyms for CVX holders after they lock their CVX tokens and signs these pseudonyms.
-
Counters: Responsible for calculating and verifying the voting results, and publishing the results and proofs of correct counting on snapshot, as shown in the figure below. Counters use partial decryption keys from a k-out-of-n encryption scheme.
Function Definitions
The voting scheme is defined by eight functions, namely:
- Setup
: On input of the security parameter and the relation represented as an arithmetic circuit, generate the prover and verifier key pairs , voting key pair , registrar key pair , commitment parameters from commitment setup , and public parameters .
- PseudonymRegister
: On implicit input and CVX holder identity id, randomly select a pseudonym , compute , and return , where is randomly selected from .
- Register
: On input of the CVX holder identity and , and list , add to list , compute , sign with the registrar private key to produce the signature , and then return .
- Vote
: On input of CVX holder identity , voting public key , and CVX holder private key , it generates a ballot , where . Additionally, compute a disjoint proof , where , and simulate a null ballot proof.
- ValidVote
: On input of a ballot , check if it is valid, i.e., whether this proof is correct and well-formed, by completing the verification through executing .
- Append
: On input of a ballot , according to , append to snapshot. It generates and appends one or more null ballots according to the probability distribution and . It computes and disjoint proof .
, where , and simulates the other side of CVX holder proof.
- Tally
,: On input of the public snapshot, calculate the voting results, return , where is the voting result, is the proof of correct counting, with the following steps:
- Run and return in case of failure.
- For each appearing in the ballots, calculate , where is the set of identified by .
- from each , mix the ballots , where is the number of pseudonyms , and return the mixed ballots and proof of valid mixing.
- For each and voting option , apply the privacy equivalence test (PET) and provide corresponding proof.
- Calculate the result for each voting based on the PET result and publish the proof.
- VerifyTally
: On input of ,, if all proofs are valid, return ; otherwise, return .
Implementation Phase
The flowchart of this electronic voting scheme illustrates the process of Convex’s private governance as follows.
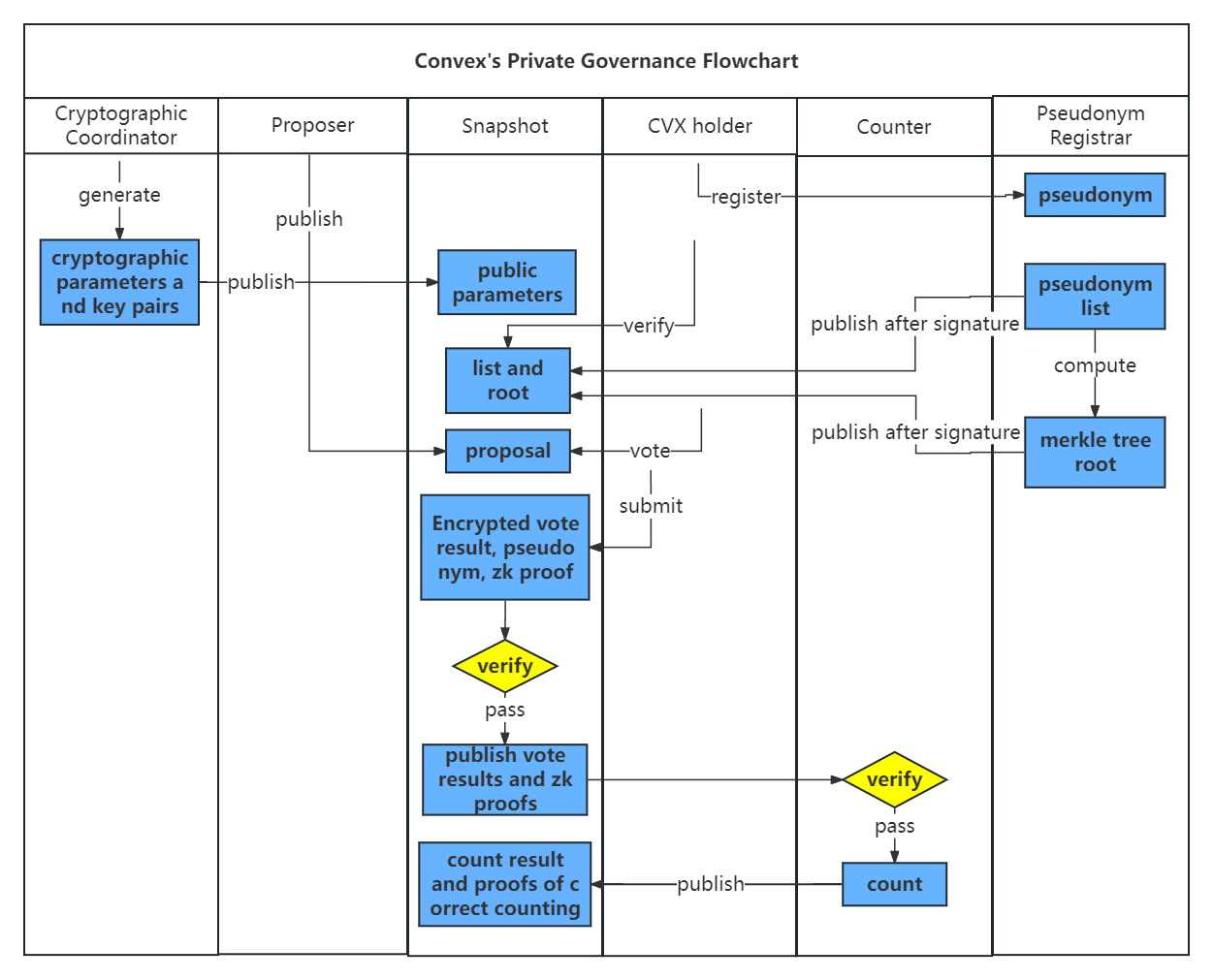
Based on this flowchart, we divide the Convex private governance process into five stages:
- Setup Phase
Given security parameters and relation , the Cryptographic Coordinator runs to:
- Generate cryptographic parameters , counting party threshold tuple , voting key pair , registrar key pair , commitment function and its parameters , and the zero-knowledge proof key pair for relation .
- Publish public parameters .
- Registration Phase
CVX holders run to:
- Choose a voting pseudonym .
- Compute using and store locally.
- Send to the pseudonym registrar via an authentic channel.
- The pseudonym registrar adds to the pseudonym list .
- Compute the merkle tree root based on the commitment order in list .
- Finally, sign and and publish them on snapshot.
- CVX holders verify and merkle tree root .
- Voting Phase
To cast a vote , CVX holders run , where , including:
- Compute , where is a random value for encryption. In the case of revoking a previous vote and voting for , CVX holders set .
- Calculate zero-knowledge proof using proving key :
- Submit to snapshot via an anonymous channel.
- Snapshot runs , checks the validity of the proof on the ballot, and verifies if the ballot already exists on snapshot.
- Snapshot runs , appending the ballot and null ballots to snapshot.
- CVX holders verify if is appended to snapshot.
- Snapshot generates null ballots as follows: Calculate , choose a from on the snapshot, compute :
- Counting Phase
Counters run , including:
- Verify ballots on snapshot and select those with valid proofs.
- Apply the homomorphic properties of the encryption scheme to calculate the final ballot for each on the snapshot.
- Shuffle, mix, and publish the final ballots without , providing proof of correctness.
- Apply PET to the final ballots and select encrypted votes from the voting.
- Decrypt ballots and publish results and decryption proofs on snapshot.
- Verification Phase
Anyone can verify the correctness of the counting by running , which verifies the results and all proofs published during the counting process. This implementation achieves large-scale electronic voting while ensuring anonymity, security, and reliability.
Compression
Recursive zk-SNARKs allow a prover to put "more knowledge" into a proof while ensuring that these proofs can still be verified by a verifier in constant or poly-logarithmic time. Using recursive zk-SNARKs as an "aggregator" of information enables independent "aggregation" of more computations than the largest (non-recursive) circuit can handle. More about recursive zk-SNARKs.
Future Work
-
Performance and Scalability: As the number of voters increases, the system's performance and scalability will face challenges. Future research could focus on the study of fully recursive zk-SNARKs to support larger-scale elections.
-
User Friendliness: An important task in promoting ZK technology is to address the current complexity of the system for ordinary users. Simplifying user interfaces and operational processes, and lowering the barrier for user adoption, will contribute to the widespread acceptance and adoption of the system.
-
Compliance and Legal Challenges: Decentralization and compliance have always been antonyms; typically, only the government can prove your identity. However, this leads to the possibility of data being tampered with at the source (but if this identity is recognized by the government, then even the fake becomes real). ZK cannot solve the problem of a trusted source, but we might need to consider: what kind of world it would be if I could prove I am who I am.
If you are interested in integrating ZK technology into your project governance to enhance privacy, scalability, and achieve governance innovation, ZEROBASE offers end-to-end ZK services and comprehensive solutions. By collaborating with us, you can explore the extensive applications of ZK technology in project governance, providing the community with a more secure, transparent, and efficient electronic voting system.